 The Hyper Tree Signature (SIG_HT)
The Hyper Tree Signature (SIG_HT)
The FORS public key is input to the bottom layer of the hypertree using the WOTS+ algorithm. This results in the value ht_sig[0],
a value of $35n$ bytes. An authentication path is derived for this to the root of this subtree (3 levels).
This root value of this subtree is passed up as input to the next tree, and so on for all 22 subtrees.
The final root of the hypertree is published as part of the public key.
When verifying a signature, the calculated root of the hypertree should match this pre-trusted root value.
Recap on WOTS+ signature | The first WOTS+ signature | First authentication path | Second HT subtree layer 1 | Tree addresses and leaf indexes going up the HT tree | Generate the SPHINCS+ Public Key Root | Contact us
Recap on WOTS+ signature
Given the Winternitz parameter, $w$, and the security parameter, $n$, we compute $len = len_1 + len_2$ where
$len_1 = \lceil 8n/\log(w) \rceil, \quad len_2 = \lfloor \log(len_1 \cdot (w-1))/\log(w) \rfloor + 1$.
In our case with $w=16$ and $n=16$, we obtain $len_1 = 32$ and $len_2 = 3$ giving $len = 35$.
An input message $m$ is interpreted as $len_1$ base-$w$ integers $m_i$, between $0$ and $w-1$. A checksum is computed, $C = \sum_{i=1}^{len_1}(w -1 - m_i)$ over these values, represented as a string of $len_2$ base-$w$ values $C=(C_1, \ldots, C_{len_2})$.
In our example, the input is broken up into 32 blocks of $\log_2(w)=4$ bits and a checksum is computed over these values and broken up into three 4-bit blocks. These blocks are interpreted as integers, denoted $m_0, m_1, \ldots, m_{34}$.
We have a WOTS private key, $sk_0, sk_1, \ldots, sk_{34}$. These values can be computed using SK.seed and the ADRS.
The signature is $\sigma_0, \sigma_1, \ldots, \sigma_{34}$, where $\sigma_i = F^{m_i}(sk_i)$. This is published in the SPHINCS+ signature value.
The WOTS public key is $pk_0, pk_1, \ldots, pk_{34}$, where $pk_i = F^{w}(sk_i)$. This can either be derived (by anyone) from the signature or directly (by the signer) from the secret keys.
Well that's the conventional theory as described by Merkle [MER79]. In practice, in the SPHINCS+ algorithm, $F$ is only applied $w-1$ times, not $w$. That is $pk_i = F^{w-1}(sk_i)$. This works just as well and reduces the number of hash computations.
The first WOTS+ signature
To compute a WOTS+ signature, we split up the input into $len_1=32$ blocks of $\log_2(w)=4$ bits, and append a checksum of length $len_2 = 3$ blocks.
Input=dd84d9c7667367183c4826ce1e1d0048
Input blocks = 0xd, 0xd, 0x8, 0x4, ..., 0x4, 0x8
checksum = 0x0ff = 0x0, 0xf, 0xf
Final blocks = 0xd, 0xd, 0x8, 0x4, ..., 0x4, 0x8, 0x0, 0xf, 0xf
= 13, 13, 8, 4, ..., 4, 8, 0, 15, 15
For each integer of value $m_i$ $(0 \le i \lt 35)$ we compute the secret key $sk_i$ and then compute $F^{m_i}(sk_i)$, the value of $F$ iterated $m_i$ times on $sk_i$.
sk[i] = PRF(SK.seed, ADRS) = SHA256(SEED || ADRS_c)For the first WOTS+ private key, at tree address
0x28daecdc86eb8761 and leaf index 6, we have
SK.seed = 7c9935a0b07694aa0c6d10e4db6b1add adrs_c = 0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000000 wots_sk[0] = PRF(SK.seed, ADRS_c) = c04623124dfcdcb1de0ad8cfc68ebf73Now we compute $F^{13}(sk_0)$ noting that
ADRS changes on each iteration
i=0 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000000 in=c04623124dfcdcb1de0ad8cfc68ebf73 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=9bd58ef09fb2991505beadf374547728 i=1 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000001 in=9bd58ef09fb2991505beadf374547728 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=5b692f1817de0cda43f1a268f47f25a8 i=2 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000002 in=5b692f1817de0cda43f1a268f47f25a8 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=9adb47261aba690966efc1b7e156f294 i=3 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000003 in=9adb47261aba690966efc1b7e156f294 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=1751b9f95e1ebd08930e66dff9e28f54 i=4 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000004 in=1751b9f95e1ebd08930e66dff9e28f54 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=6f2a71a8348d930f8a9d87b7c18dd8ad i=5 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000005 in=6f2a71a8348d930f8a9d87b7c18dd8ad F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=1467f55ed3d05c38dc4f1452367ecbee i=6 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000006 in=1467f55ed3d05c38dc4f1452367ecbee F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=1ba258fd7ea69fd9776f758ba61c36c0 i=7 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000007 in=1ba258fd7ea69fd9776f758ba61c36c0 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=09a598897a4cb35c2de65f269e14863a i=8 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000008 in=09a598897a4cb35c2de65f269e14863a F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=aa175ead7c15503959fdaa6435fa4002 i=9 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000009 in=aa175ead7c15503959fdaa6435fa4002 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=28bb18f9c877c58af991bd22dbb5dc7a i=10 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb87610000000006000000000000000a in=28bb18f9c877c58af991bd22dbb5dc7a F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=1d558b4e17b9396f4a845a349ad5a9b8 i=11 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb87610000000006000000000000000b in=1d558b4e17b9396f4a845a349ad5a9b8 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=b6900ec504eed70cea23e7bea3f90ce1 i=12 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb87610000000006000000000000000c in=b6900ec504eed70cea23e7bea3f90ce1 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=cb56a9488bb970ce78a2623db324b873 ht_sig:cb56a9488bb970ce78a2623db324b873Hence the first value in the HT signature,
cb56a9488bb970ce78a2623db324b873 #ht_sig[0][0]
This procedure is repeated for all 35 integers $m_i$.
For $i=34=\text{0x}22$ we have
ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000002200000000 wots_sk[34] = PRF(SK.seed, ADRS_c) = cd9f6b2eba904236a7a45087be823ff6and $m_{34}=15$ so we compute $F^{15}(sk_{34})$
i=0 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000002200000000 in=cd9f6b2eba904236a7a45087be823ff6 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=5f88200ab55730f6484afa248575820a i=1 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000002200000001 in=5f88200ab55730f6484afa248575820a F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=73bb1db5f1d5080709efe3471e3e62f6 ...[CUT]... i=14 ADRS=0028daecdc86eb87610000000006000000220000000e in=a36463a260ce723ce650e4b714bf5175 F(PK.seed, ADRS, in)=a0154e91a720b96b0d738d05405e6f48
Hence
a0154e91a720b96b0d738d05405e6f48 #ht_sig[0][34]
ht_sig[0]:
cb56a9488bb970ce78a2623db324b873 # ht_sig[0][0] 33b9c30d9c6f9400868677c2dac9ee60 # ht_sig[0][1] # [...CUT...] a0154e91a720b96b0d738d05405e6f48 # ht_sig[0][34]
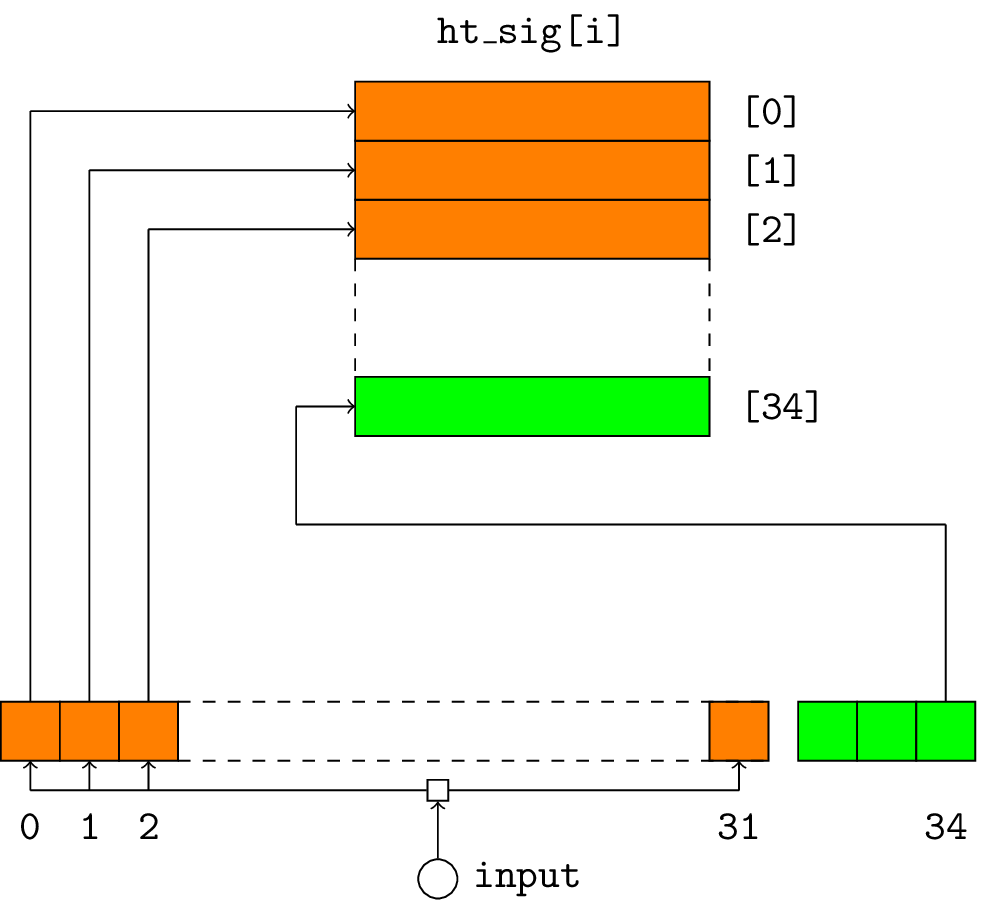
The input is either the root of the lower HT tree root[i-1] or the FORS public key for the bottom HT tree at layer 0.
The input is split into 32 4-bit blocks (shown orange) and the 3 x 4-bit checksum is shown in green.
First authentication path
For the WOTS+ algorithm in our example, we have $len=35$.
NOTE: the computations of the WOTS+ public key and the authentication path are completely independent of the HT signature value. They depend solely on the tree address of the WOTS+ subtree.
The WOTS public key is computed by calculating $F^{w-1}(sk_i)$ for $0\le i \lt 35$ and concatenating the 35 $n$-byte values.
NOTE: although the documentation says "The corresponding public key is derived by applying $F$ iteratively for $w$ repetitions to each of the $n$-bit values in the private key", in practice, it is only repeated $w-1$ times. This is the case both in the chain algorithm as described in the specification and in the reference implementation. This doesn't affect the end result - all the principles of the Winternitz algorithm still work. It does reduce the number of hash computations by one.
The 560 bytes of the WOTS public key are compressed using $T_{len}$ to obtain the $n$-byte leaf value.
For our example at layer 0 with tree_address=0x28daecdc86eb8761 and tree_idx=6 we generate
the WOTS+ private key and then use the chain function to compute the corresponding WOTS+ public key
$pk = F^{w-1}(sk)$.
Generate WOTS+ private key for subtree[0] ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000000 sk[0]=c04623124dfcdcb1de0ad8cfc68ebf73 Compute pk using chain... adrs=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000000 F(0)= 9bd58ef09fb2991505beadf374547728 adrs=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000000000001 F(1)= 5b692f1817de0cda43f1a268f47f25a8 ..[CUT]... F(14)= aff586153b484118f05accd6e7bde2a3 pk[0]=aff586153b484118f05accd6e7bde2a3 Generate WOTS+ private key for subtree[1] ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000100000000 sk[1]=5ae611d347f988308958c414f865c942 Compute pk... ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000000100000000 pk[1]=0a7e84c64a9d47f3a9ec13092c2b68dc ...[CUT].. Generate WOTS+ private key for subtree[34] ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000002200000000 sk[34]=cd9f6b2eba904236a7a45087be823ff6 Compute pk... ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876100000000060000002200000000 pk[34]=a0154e91a720b96b0d738d05405e6f48 wots_pk (560 bytes): aff586153b484118f05accd6e7bde2a3 0a7e84c64a9d47f3a9ec13092c2b68dc ff648dce82a1e3602c736bae67fc0ec8 ...[CUT]... a0154e91a720b96b0d738d05405e6f48 Compress wots_pk ADRS=0028daecdc86eb876101000000060000000000000000 leaf=56c1cd468c05d6b5a9ad57e87c4edf12
This calculation is repeated for each of the other 7 leaves in this subtree in order to calculate the authentication path.
For layer=0 the authentication path from the leaf to the subtree root can be computed,
and this $3n$-byte value is added to the signature value:
b1f67e538bb9d4c2ef860f50085bcb72 # ht_auth_path[0] c10fb38ab696949b9417ddbefe8e4cad 77a2617d410d8f1acd1fbc29830e1a51
The root of this subtree is f2ec3b2ae23a50355d057b97df65c8bc.
This is passed as input to the next-higher WOTS+ subtree at layer 1.
tree_address.
Each subtree in the hypertree has height $h' = h/d = 66 / 22 = 3$, and has $2^{h'} = 8$ leaves.
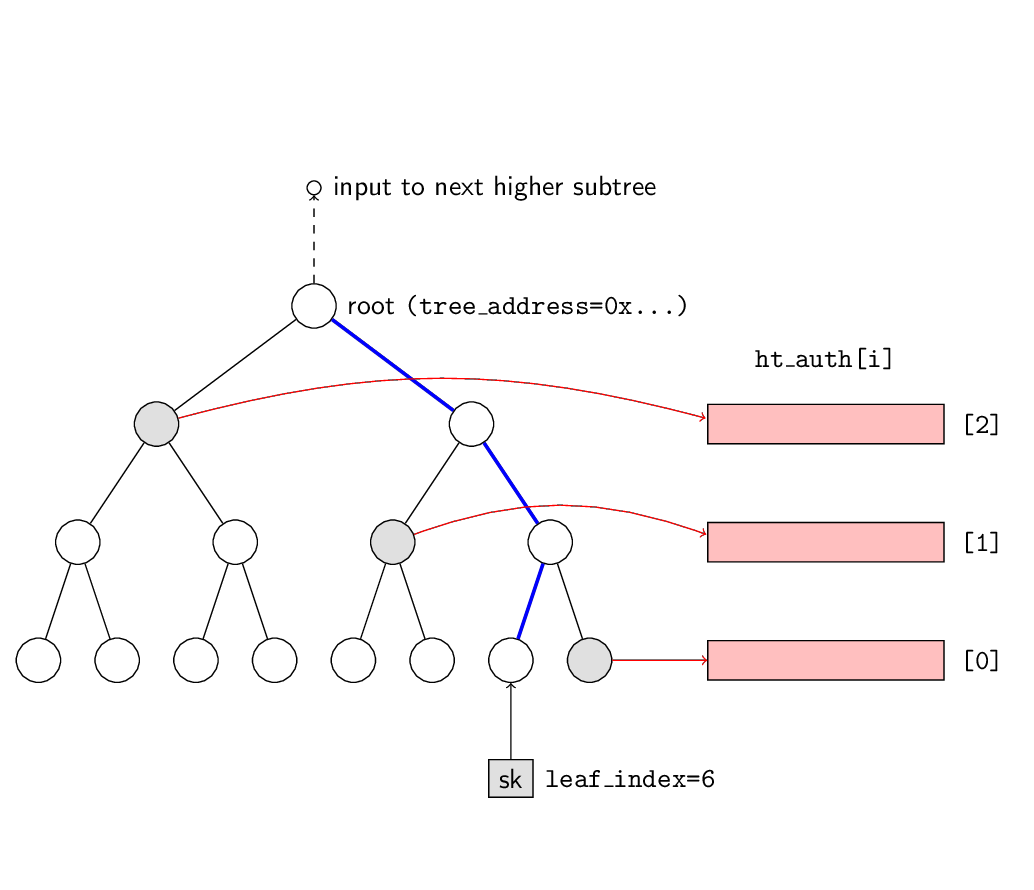
leaf_index=6 are shown shaded in grey and their node values are output to the signature in order
$[0], [1], [2]$. The value of the root node is passed as input to the next higher subtree.
Note that the values of all 8 leaves at height 0 must be calculated to compute the authentication path and root.
Second HT subtree layer 1
leaf_index = tree_address & (2^3 - 1) = 0x28daecdc86eb8761 & 0x7 = 1 tree_address = tree_address >> 3 = 0x28daecdc86eb8761 >> 3 = 0x51b5d9b90dd70ec
Note that the terms tree_index and leaf_index are used interchangeably
(and, just to confuse, this value is used to set the KeyPairAddress in the ADRS!).
01 051b5d9b90dd70ec 00 00000001 00000000 00000000
The input to be signed using the WOTS+ algorithm is the root of the lower subtree f2ec3b2ae23a50355d057b97df65c8bc.
Applying the WOTS+ signature algorithm, we obtain the second HT signature ht_sig[1]:
13a4d0d6844aa68b6cf03467374be19a # ht_sig[1][0] 3ed2d9e45dc9cee2353b80b9bdeda69b # ht_sig[1][1] #...[CUT]...] 72baa36f9bebef31bd03c1fa9f8fd891 # ht_sig[1][34]
150d6ff09ca91ddf2411d40d6cdb428b # ht_auth_path[1] 026a5503246178066c93cc0092dfb834 d31eba4a04674ee4689fb4e3ed25bff1The root of this subtree is
9c70e81c7715d68e547b77807644cb8b, which is passed as input to the next layer.
And so on and so forth up until layer 21 where we have the 22nd HT signature:
422d9bc577f69260607d7d4a8c56d85f # ht_sig[21][0] ab5bcb9675f1f0dd7904e1d07e95fef3 # ht_sig[21][1] #...[CUT]...] ba402da2746963d2d8b12f8abf5d86ad # ht_sig[21][34]and the authorization path
fa1ef7c928518b1afdebddd1b83a3b66 # ht_auth_path[21] 5fae6d71863b4207d39e61823b59c6a9 220f10bd9e03c371b229a79489601278
This is the end of the signature value.
The root of the top-most subtree is 4fdfa42840c84b1ddd0ea5ce46482020
and this should equal the public key root PK.root, which can be computed independently.
Tree addresses and leaf indexes going up the HT tree
0x28daecdc86eb876 and leaf index is 6 (see step 2 here).
The subsequent indexes are computed as follows:
leaf_index[i] = tree_address[i-1] & 0x7 # (2^3 - 1) tree_address[i] = tree_address[i-1] >> 3Giving the following base ADRS values:
layer= 0,ADRS=00 28daecdc86eb8761 00 00000006 00000000 00000000 layer= 1,ADRS=01 051b5d9b90dd70ec 00 00000001 00000000 00000000 layer= 2,ADRS=02 00a36bb3721bae1d 00 00000004 00000000 00000000 layer= 3,ADRS=03 00146d766e4375c3 00 00000005 00000000 00000000 layer= 4,ADRS=04 00028daecdc86eb8 00 00000003 00000000 00000000 layer= 5,ADRS=05 000051b5d9b90dd7 00 00000000 00000000 00000000 layer= 6,ADRS=06 00000a36bb3721ba 00 00000007 00000000 00000000 layer= 7,ADRS=07 00000146d766e437 00 00000002 00000000 00000000 layer= 8,ADRS=08 00000028daecdc86 00 00000007 00000000 00000000 layer= 9,ADRS=09 000000051b5d9b90 00 00000006 00000000 00000000 layer=10,ADRS=0a 00000000a36bb372 00 00000000 00000000 00000000 layer=11,ADRS=0b 00000000146d766e 00 00000002 00000000 00000000 layer=12,ADRS=0c 00000000028daecd 00 00000006 00000000 00000000 layer=13,ADRS=0d 000000000051b5d9 00 00000005 00000000 00000000 layer=14,ADRS=0e 00000000000a36bb 00 00000001 00000000 00000000 layer=15,ADRS=0f 00000000000146d7 00 00000003 00000000 00000000 layer=16,ADRS=10 00000000000028da 00 00000007 00000000 00000000 layer=17,ADRS=11 000000000000051b 00 00000002 00000000 00000000 layer=18,ADRS=12 00000000000000a3 00 00000003 00000000 00000000 layer=19,ADRS=13 0000000000000014 00 00000003 00000000 00000000 layer=20,ADRS=14 0000000000000002 00 00000004 00000000 00000000 layer=21,ADRS=15 0000000000000000 00 00000002 00000000 00000000
Generate the SPHINCS+ Public Key Root
-
The SPHINCS+ Public Key Root
PK.rootcan be computed from just the top-most HT subtree. -
Crucially, all leaf nodes of all intermediate trees are deterministically generated WOTS+ public keys that do not depend on any of the trees below it.
-
During key generation, only the top-most subtree is computed to derive the public key.
-
In our case we have a subtree of height $h' = h/d = 66 / 22 = 3$. This has $2^{h'} = 8$ leaves.
-
Each leaf value is the compression of $len = 35$ chain heads derived from the WOTS+ private key values $sk_0, sk_1, \ldots sk_{34}$, which in turn can be derived using the PRF function with
SK.seed. -
The value of the root node can then be calculated from the 8 leaf values using the usual Merkle tree computations, but note that the value of
ADRSin the $F$ function is different each time it is called. - Note also that the value of the ADRS parameter is different when computing the secret keys for the public key root and when computing the secret keys for the signature.
Python code
See wots_gen_pk.py
['505df0061b7e0041c8501bc5030ad439', '7bd5deb67217d33505043e204d88f687', '03b03bb327c9b48beab7722c4d5eb906', 'fa1ef7c928518b1afdebddd1b83a3b66', '44b4dad150fdf64b6aa7fab1aea016e6', '0913211acf332a24629915d1b8226ff2', 'a8fca106e9c1263dda280988f59f13e2', '84035916aba8e0b92f73364d4bb50a18']
Using the usual Merkle tree calculations, these give the root value of 4fdfa42840c84b1ddd0ea5ce46482020,
which equals PK.root.
sk[0]..sk[34] and the corresponding public keys $pk[i]=F^{w-1}sk[i]$
leaf_idx=0 15000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 sk[0]=a7454d518762bb8f597e6771a7f427a4 adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 F(0)= be98aae3fe3492e747036374de5ec7f5 adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000000000000001 F(1)= 0da9010a810c205f74445334234ebb32 # ...[CUT]... F(13)= a7e250e3fa99c00e13140b99b7ebac77 adrs=1500000000000000000000000000000000000000000e F(14)= f3a6275658f3be797af7022736613710 pk=f3a6275658f3be797af7022736613710
sk[1]=4463d062050a39f93180c27a4fa66531 adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000000100000000 F(0)= ce7f6953e4bcbcf24a00d43f1830c66f adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000000100000001 F(1)= 161e90958f09d10f903c6f07b5220fef #...[CUT]... adrs=1500000000000000000000000000000000010000000e F(14)= e8c6f3a192da61398228d3abb09452a2 pk=e8c6f3a192da61398228d3abb09452a2and so forth up to the 35th key
sk[34]=d623b7cec3eb4370b31a357ec48039f3 adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000002200000000 F(0)= e1d53a93e1a2b98f750eb750701129a5 adrs=15000000000000000000000000000000002200000001 F(1)= e86da17e6c47e434ddeed7196ff73798 #...[CUT]... adrs=1500000000000000000000000000000000220000000e F(14)= 5962475912c4f1408d895c2de893f375 pk=5962475912c4f1408d895c2de893f375All these 35 public keys (560 bytes) are compressed using
T_len
Input to thash:
f3a6275658f3be797af7022736613710
e8c6f3a192da61398228d3abb09452a2
6e5f2ec95f2b903d74df263eeb816a9a
4c80523878fcf94f0abcc3cb9afa759e
2794860e20ffa9f9901f084fb57b379b
8b8dc6e63c0baa544047be73dfa861f5
5b7339d418777ba31d711fff92aae2ea
ae886fe4595bd13866622cd478497f1d
54e1ad2aa941c6ddf6b27a0eda455840
acb2073ab47bd4969b59d0c2eab24ada
c8b43df1c6b38170cbff50312e6d5b47
7075f937cb8d318dded66bdacfcee3d5
f58f8b3b85c166f1c321d1f07ae1edaa
5bb09a87117b0275147021c9dff22003
a92809dca3d0c1265c0e161332fe713d
781a2566c46ff520446251b814984429
e8cec559c61767fdf6d6f64f18470e20
1e463e1f7b6fb4807e76fb2a8edd986c
a6beb33be54f3e811c17ef2638b447c7
b2182bee63b7046cc85d32961c43dd86
f093a3656dcbdded9af6fef34a2f240f
bd64377a76da737e413ccd83092f3ce9
5c740b3f559000bbb383c8ca8fee22e4
6ae3c21a1434df261f415099a4ba5077
f879cf1c55933ce43361b501a9012d7d
78de6af22199e8e12c6e6e817f73dfb1
290c2176b2b22db350687710b0fe205c
7ec4470e93b95610ab219e790781d1a5
0e16520a2b411daac2189153107fec81
e71022dffb186c5cfbbeb1a75041aefb
00d7acf160aa380e870bcb002bd45c11
e4ccf58ff81f2b07ac4f499176fe6111
2e5a5905419c98c11047c34e4cd38059
2e83dafcd04ae0c4e1a300e661e3aade
5962475912c4f1408d895c2de893f375
wots_pk_addr=15000000000000000001000000000000000000000000
leaf[0]=T_len(PKseed, adrs, input)
=505df0061b7e0041c8501bc5030ad439
The above calculations are repeated for the other seven leaf values leaf[1]...leaf[7] of the top-most tree,
and then the root value of the tree can be computed.
| << previous: Computing the FORS signature | Contents | next: SPHINCS+ Python Code >> |
Rate this page
Contact us
To comment on this page or to contact us, please send us a message.
This page first published 17 March 2023. Last updated 9 September 2025.

